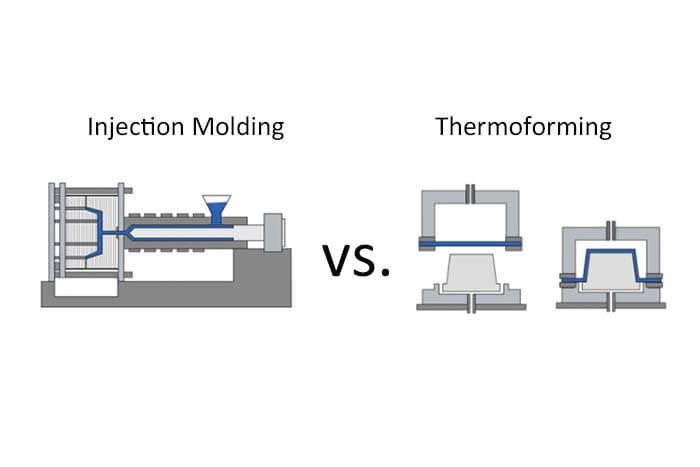
Manufacturers, OEMs, and product teams often reach a point where they must choose between two major plastic-forming processes: injection molding and thermoforming. Both methods are widely used, both deliver reliable commercial parts, and both support industries ranging from consumer goods and automotive to medical devices and industrial equipment.
But they serve very different purposes.
If you are launching a new product, scaling production, or comparing options for tooling, cost, precision, or material selection, understanding these differences is essential. And if you’re sourcing U.S.-based production, especially in the Houston and The Woodlands region, selecting the right process can determine whether your program succeeds or runs into unnecessary delays and expenses.
Below is a clear, engineering-focused explanation of how injection molding and thermoforming differ, why OEMs typically choose one over the other, and how Haumann Group supports companies across Texas and nationwide.
What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a steel or aluminum mold under high pressure, cooled, and ejected as a solid part.
It is the preferred choice for parts that require:
- Tight tolerances
- Complex geometries
- High repeatability
- Fine surface finishes
- Long-term production scalability
Injection molding is used for millions of components across consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive systems, agricultural products, industrial equipment, household appliances, and more.
At Haumann Group, our Houston-based facility provides complete, end-to-end injection molding solutions, from engineering and tooling to full-scale production.
What Is Thermoforming?
Thermoforming is a technique that involves the heating of a plastic sheet to a pliable state, the molding of it by using vacuum or pressure, and finally the cutting into shape of the product.
Advantages:
The method is most commonly used for:
- Large parts
- Shallow geometries
- Lightweight structural components
- Packaging trays
- Enclosures with moderate detail
Industries frequently utilizing thermoforming include packaging for consumers, industrial drama dust covers, and interior transportation, along with various protective housings.
The cost of this method is low when large pieces of surface area are concerned, but on the other hand, it cannot give the precision or complexity that injection molding can offer.
Tooling Differences; Cost, Durability & Speed:
Tooling is often the single biggest factor in selecting a process.
Injection Molding Tooling:
Injection molds are CNC-machined from steel or aluminum and can last anywhere from tens of thousands to millions of shots.
Advantages:
The application of this technique has many significant advantages:
- Supports high-volume production
- Produces highly detailed features
- Enables consistent dimensional accuracy
- Supports complex undercuts, threads, snaps, and inserts
The investment in tooling is higher since injection molds are more complex. However, the per-part cost becomes incredibly low at the large scale.
Thermoforming Tooling:
Thermoforming tools are much simpler, often made from machined aluminum, cast tooling, or polymer tooling.
Advantages:
- Lower upfront cost
- Faster to build
- Suitable for prototypes or moderate-volume production
- Great for large, shallow components
However:
- Limited detail
- Lower repeatability
- Shorter tooling lifespan
OEMs who need millions of identical parts almost always choose injection molding.
Material Differences: Pellets vs Sheets:
The material format is another important difference between these two procedures.
Injection Molding Materials:
Plastic pellets are used in the procedure of injection molding. This gives access to many thousands of engineering-grade resins, some of which are:
- ABS
- PC
- PP
- Nylon
- PE
- TPU
- High-heat, medical, automotive, and flame-rated materials
This opens up:
- Strength improvement
- Impact resistance
- Heat tolerance
- Chemical resistance
- UV stability
- Color matching
- Reinforced or filled materials
This is one of the reasons why OEMs in the automotive, medical, aerospace, and electronics industries are so heavily dependent on injection molding.
Thermoforming Materials:
Thermoforming is a process of cutting plastic sheets, which also results in limited material choices.
The most common sheet materials are:
- ABS
- HIPS
- PETG
- Acrylic
- Polycarbonate(sheet-grade)
- HDPE
Sheets cannot be able to offer the same strength-to-weight or engineering performance as resin-based molded parts.
Precision & Part Quality:
Injection Molding: High Accuracy
Injection molding uniformly provides:
- Tight tolerances
- Sharp features
- Crisp edges
- Textured or cosmetic surfaces
- Repeatability across millions of units
This is the reason complex components, brackets, housings, connectors, covers, enclosures, and device casings are mostly always injection molded.
Thermoforming; Medium Accuracy:
Thermoformed parts are:
- Less precise
- Limited in sharp detailing
- More prone to thickness variation
- Not suitable for intricate internal structures
They mostly work very well for large protective shells or covers, not precision-engineered parts.
Cost Differences: When Each Process Is More Cost-Effective:
Injection Molding:
Best for:
- High-volume production
- Parts requiring precision
- Programs where long-term per-unit cost matters
- Tooling: Higher
- Per-part price: Very low at scale
Thermoforming:
Best for:
- Large parts
- Low-volume runs
- Prototyping or early-stage testing
- Tooling: Lower
- Per-part price: Higher
OEMs usually use thermoforming early in development and switch to injection molding once demand increases.
Why OEMs Choose Injection Molding for Complex Parts:
OEMs, engineers, and product development teams select injection molding when they need:
- Complex geometries
- Internal support ribs
- Snap fits or interlocks
- Tight tolerances
- High-strength engineering plastics
- Consistent part-to-part repeatability
- Long production lifespan
Products such as medical housings, consumer electronics shells, automotive interior components, appliance enclosures, and structural parts all rely on injection molding. Thermoforming cannot replicate this level of precision or durability.
Why Houston Manufacturers Prefer Haumann Group:
Texas manufacturers, especially those in Houston, The Woodlands, Conroe, Sugar Land, and the surrounding areas, seek domestic manufacturing partners who understand both engineering and production requirements.
Haumann Group provides:
- U.S.-based engineering and production
- Fast lead times
- Local communication and onsite support
- Low, medium, and high-volume capabilities
- In-house tooling
- ISO-level quality
- Competitive pricing
- Reliable sourcing and supply-chain stability
Whether you are manufacturing a simple cover or a multi-part assembly, our team delivers consistent quality from concept through mass production.
How to Choose the Right Process for Your Product:
When choosing between injection molding and thermoforming, consider the following:
Choose Injection Molding If You Need:
- Complex features
- Tight tolerances
- High-strength plastics
- Long-term manufacturing
- Cosmetic surfaces
- Snap fits, threads, or inserts
- High-volume production
- Engineering-grade materials
Choose Thermoforming If You Need:
- Large, simple parts
- Fast, affordable tooling
- Low production volume
- Lightweight structural panels
- Moderate cosmetic quality
If you are not sure, Haumann Group can evaluate your design and help determine the optimal method.
FAQs: Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming:
1. Which process is more cost-effective?
Thermoforming is usually cheaper for tooling, while injection molding gets more cost-effective for mid to high production volumes.
2. Which method is better for complex parts?
Injection molding offers superior precision, detail, and consistency.
3. Can thermoforming get tight tolerances?
No. Thermoforming is suitable for general shapes, not intricate features.
4. Which industries rely on injection molding?
Automotive, medical, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, appliances, and some other products.
5. Does Haumann Group support both low and high volume?
Yes. We support startup runs, bridge production, and full-scale mass manufacturing.
Conclusion: Get Expert Guidance from Haumann Group (Houston, Texas):
If you’re deciding between injection molding and thermoforming, our engineering team can review your design, evaluate requirements, and recommend the best solution for your product.
Haumann Group proudly serves Houston, The Woodlands, and customers nationwide with reliable, U.S.-based manufacturing, complete tooling, and high-quality plastic production.
Serving Houston, The Woodlands, and nationwide U.S. brands
- Contact us today
- Request a quote
- Visit: haumann-group.com